Gum Health Matters: Understanding Periodontal Disease and Prevention
It is crucial to prioritize gum health by learning about and preventing periodontal disease.
Gum Health
13 September 2023
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the often overlooked yet crucial aspect of oral health – your gums. Beyond just teeth, the health of your gums plays a pivotal role in maintaining a radiant smile and overall well-being. In this blog, we’ll delve into periodontal disease: what it is, how it develops, and most importantly, how you can effectively prevent it. Get ready to empower yourself with the knowledge that will help you safeguard your gum health and preserve your beautiful smile for years to come.
What is Periodontal Disease?
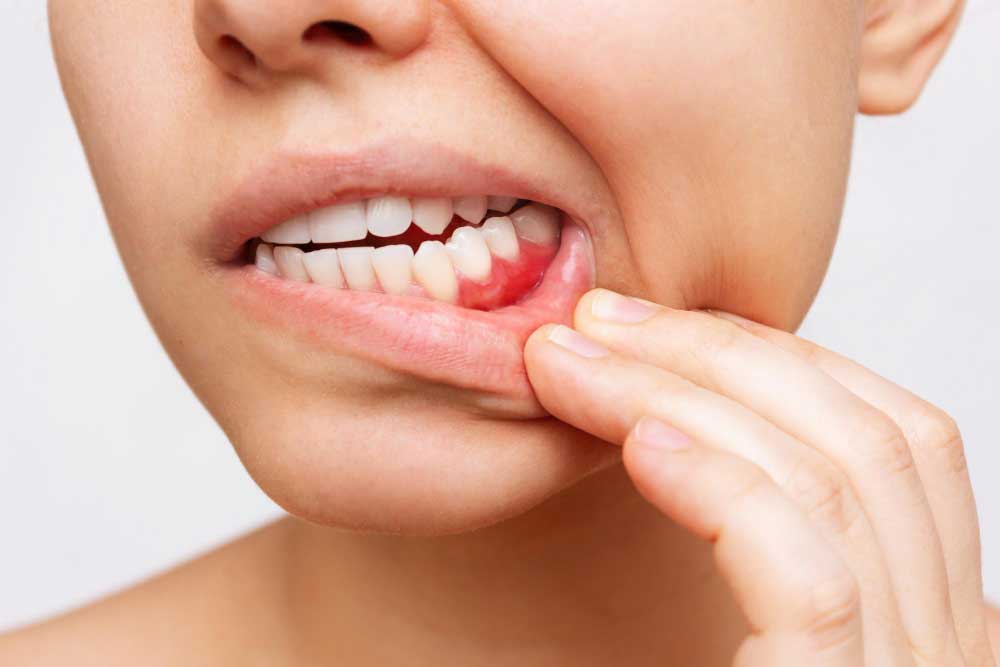
Periodontal disease, commonly called gum disease, is an intricate oral health condition that goes beyond your teeth, impacting the supporting structures of your mouth. This condition originates with the accumulation of bacteria on your teeth’s surface, forming a sticky film known as plaque. If not properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to inflammation and infection of the gums.
The progression of periodontal disease occurs in stages, each with distinct characteristics and potential consequences. Understanding these stages is crucial for recognising the signs early and taking proactive steps to prevent further deterioration.
Stages of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease progresses through distinct stages, each marked by specific symptoms and levels of damage. Recognising these stages is crucial for addressing the issue promptly and preventing further deterioration of your gum health.
1. Gingivitis:
Gingivitis marks the initial stage of periodontal disease. It’s characterised by the inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of plaque – a sticky film of bacteria – along the gumline. Key features of gingivitis include:
Redness and Swelling:
Gums appear redder than usual and may be swollen due to increased blood flow to the affected area.
Bleeding Gums:
Gums may bleed when brushing or flossing, indicating inflammation and sensitivity.
Mild Discomfort:
Some individuals might experience mild discomfort or tenderness in the gums. While gingivitis is the earliest stage and is often mild, it shouldn’t be ignored. Prompt attention and improved oral hygiene can reverse these symptoms and prevent the disease from progressing.
2. Periodontitis:
When gingivitis isn’t addressed, it can advance to periodontitis. At this stage, the infection extends beyond the gumline and affects the underlying structures that support your teeth. Key characteristics of periodontitis include:
Formation of Pockets:
As the gums pull away from the teeth, pockets form between the teeth and gums. These pockets become breeding grounds for bacteria.
Increased Gum Recession:
The gums recede further, exposing more of the tooth’s surface and tooth roots.
Loss of Bone:
The bone that supports the teeth starts to break down due to the ongoing infection, leading to a compromised foundation for your teeth. During periodontitis, the damage becomes more severe, and it’s important to seek professional intervention to prevent further harm.
3. Advanced Periodontitis:
It is the most critical stage of periodontal disease. The infection has now caused significant damage to the supporting bone and tissues, leading to serious consequences:
Tooth Mobility:
Teeth can become loose and might shift position due to loss of bone and gum tissue support.
Visible Changes:
Changes in teeth alignment and noticeable gaps between teeth become more evident.
Increased Tooth Sensitivity:
Tooth roots, now exposed to receding gums, can cause heightened sensitivity to hot and cold substances.
Risk of Tooth Loss:
Without proper treatment, teeth can become so destabilised that they might need to be extracted.
Advanced periodontitis requires immediate attention from a dental professional. Treatment can involve more intensive procedures to halt the progression of the disease and salvage your oral health.
Understanding the stages of periodontal disease empowers you to take action at the earliest signs of trouble. By prioritising regular dental care and practising effective oral hygiene, you can maintain healthy gums and a strong foundation for your smile.
Causes of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease doesn’t have a single cause; instead, it arises from a combination of factors that can increase your susceptibility to gum problems. Understanding these causes can help you make informed choices to maintain your gum health.
- Poor Oral Hygiene:
Inadequate oral hygiene is a primary contributor to the development of periodontal disease. When plaque isn’t consistently removed through proper brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which is more difficult to remove and harbours harmful bacteria.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use:
Tobacco use, including smoking, significantly increases the risk of gum disease. Smoking weakens the immune system’s response to infections, making it harder for your body to fight the bacteria causing gum inflammation.
- Genetic Predisposition:
Genetics can play a role in your susceptibility to periodontal disease. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition, making them more prone to gum issues. It underscores the importance of thorough oral care if you have a family history of gum disease.
- Diabetes:
Diabetes can impact your body’s ability to control blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of infections, including gum infections. Conversely, untreated gum disease can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels, creating a two-way relationship.
- Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause, can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, which makes it crucial to maintain excellent oral hygiene during these times.
- Medications:
Certain medications, such as those for high blood pressure, depression, and certain heart conditions, can have side effects that reduce saliva flow. Saliva is vital in cleansing the mouth; decreased saliva can contribute to gum disease.
- Immune System Problems:
A compromised immune system, whether due to illnesses like HIV/AIDS or medical treatments like chemotherapy, can weaken your body’s ability to fend off infections, including gum infections.
Preventing periodontal disease involves addressing these risk factors. Adopting a thorough oral hygiene routine, avoiding tobacco use, managing health conditions, and seeking regular dental care can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum problems. Proactive care is key to maintaining healthy gums and preserving oral health.
Preventing Periodontal Disease
While periodontal disease can be concerning, the good news is that there are effective strategies to prevent its onset and progression. Adopting a proactive approach to oral care and making healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease.
- Effective Oral Hygiene Practices:
- Brush Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste. Focus on the gumline, using gentle circular motions to remove plaque and food particles.
- Choose the Right Brush: Opt for a soft-bristle toothbrush to avoid damaging your gums while brushing.
- Daily Flossing:
- Floss Daily: Flossing removes plaque and debris from between teeth and along the gum line, where a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Regular Dental Check-ups:
- Schedule Check-ups: Regular dental visits are essential for professional cleanings and early detection of any signs of gum disease. Aim for biannual visits unless your dentist recommends otherwise.
- Nutritional Choices for Gum Health:
- Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins and low in sugary and processed foods. Vitamins and minerals from a well-balanced diet support gum health.
- Quit Smoking:
- Avoid Tobacco: If you smoke or use tobacco products, quitting is vital for preventing gum disease. Smoking weakens the immune system and restricts blood flow, hindering gum tissue’s healing ability.
- Managing Health Conditions:
- Control Diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range to prevent complications, including gum disease.
- Hormonal Changes: If you’re experiencing hormonal fluctuations, such as during pregnancy, prioritise impeccable oral hygiene to counter heightened gum sensitivity.
- Address Teeth Grinding:
- Consult Your Dentist: Discuss this with your dentist if you grind your teeth. Teeth grinding can place excessive pressure on your gums and teeth, exacerbating gum issues.
Remember, prevention is the cornerstone of maintaining optimal gum health. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can enjoy a confident smile and protect yourself from the potential complications of periodontal disease. Your commitment to gum health will pay off through a healthier, happier mouth.
Seeking Professional Help
Recognising the signs of gum disease and knowing when to seek professional assistance is crucial for preventing the condition from progressing to more severe stages. Prompt intervention by a dental professional like Innovative Dental can make a significant difference in preserving your gum health and overall oral well-being.
- Recognising Signs of Gum Disease:
Bleeding Gums: If your gums bleed while brushing or flossing, it’s an early indication of inflammation and potential gum issues.
Redness and Swelling: Red, swollen, or tender gums are signs of gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease.
Persistent Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath that doesn’t improve with oral hygiene might be a sign of an underlying gum infection.
Changes in Tooth Fit: If your teeth suddenly feel misaligned or there’s a change in how they fit together when you bite, it’s essential to consult a dentist.
Pockets or Spaces: If you notice pockets forming between your teeth and gums or visible gaps, it might signify periodontitis.
- Importance of Timely Dental Consultation:
Early Intervention: Dental professionals can diagnose gum disease early, allowing for less invasive and more effective treatment.
Professional Cleaning: Regular dental check-ups include professional cleanings that remove tartar and plaque buildup, reducing the risk of gum disease.
Tailored Treatment: If gum disease is detected, your dentist can recommend personalised treatment plans to address your needs.
By being attentive to changes in your gum health and seeking professional help promptly, you can prevent the progression of gum disease and its potential complications. Remember, your dental team is your ally in maintaining healthy gums and a vibrant smile throughout your life.





